

Yantai Ruihua Food Co., Ltd. is a professional enterprise dedicated to the research and production of food fillings. Established in 2005, covering an area of 28000 square meters with a total investment of over 46 million yuan.
The company is mainly engaged in the production and sales of pastries (mooncake fillings), fruit products (jam), and other food products (pre mixed pastry powder). The annual production is approximately 2500 tons.
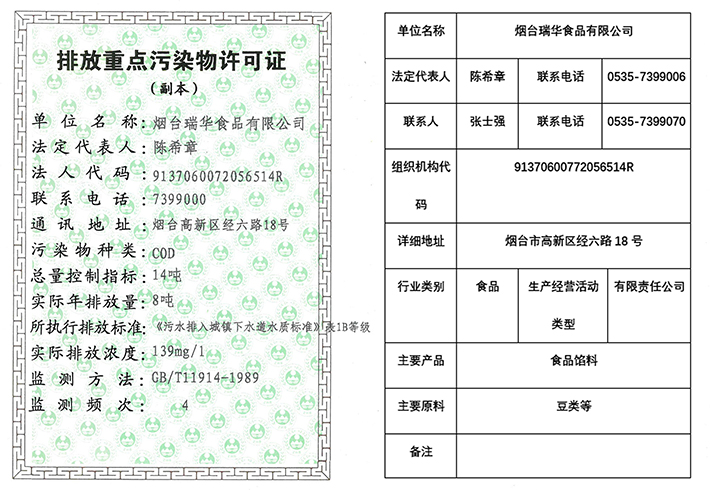
The construction of the wastewater treatment facility was approved by the Environmental Protection Bureau of Laishan District on November 3, 2008, with an environmental protection investment of 2.2 million yuan. The acceptance monitoring of wastewater treatment facilities passed the acceptance inspection of Laishan District Environmental Monitoring Station on December 5, 2011. From the monitoring results, it can be seen that the main pollution factors CODcr, ammonia nitrogen, SS, and pH in the wastewater discharged from the sewage treatment facilities of Yantai Ruihua Food Co., Ltd. all meet the comprehensive discharge standards for water pollutants in the Shandong Peninsula Basin.
The types of pollutants emitted by the company's project include COD in wastewater, which is mainly used for cleaning beans, steaming, sand washing, and equipment cleaning. The wastewater generated by the project is 87.78m ²/d and 26334m ²/a. COD wastewater online continuous monitoring devices will be installed according to the specifications, permanent sampling and discharge outlets will be set up, and a sampling and monitoring standard room will be installed. The wastewater treatment process adopts sludge production method and uses anaerobic and aerobic treatment for prevention and control. The designed processing capacity of the treatment facility is over 1200 tons per day, and the wastewater discharge outlet is installed in a standardized manner at 121 ° 31'40 "east longitude and 37 ° 24'50" north latitude and discharged to the Xin'an River sewage treatment plant. The automatic wastewater monitoring equipment has passed the acceptance inspection of Yantai Environmental Monitoring Center Station.
All production wastewater and sewage are discharged after being treated in the sewage treatment system. The CODcr discharge concentration is 500mg/l, which meets the requirements of the "Water Quality Standards for Wastewater Discharge into Urban Sewers". The total CODcr discharge of the project is 13.17t/a.
Based on relevant laws and regulations, as well as national standards such as the Environmental Protection Law of the People's Republic of China, the Water Pollution Prevention and Control Law of the People's Republic of China, the Air Pollution Prevention and Control Law of the People's Republic of China, the Work Safety Law of the People's Republic of China, the Measures for Reporting Information on Sudden Environmental Incidents by Environmental Protection Administrative Authorities (Trial), the Shandong Provincial Environmental Protection Regulations, and the Regulations on the Safety Management of Hazardous Chemicals, we have correctly responded to sudden environmental pollution accidents, ensured that on-site emergency response and disposal can be carried out quickly and effectively when accidents occur, protected the life and property safety of company employees, and prevented the occurrence of sudden environmental pollution accidents. In combination with the actual situation of our company, we have formulated an emergency plan for sudden plutonium environmental pollution accidents.
1、 Applicable scope
This plan is applicable to environmental pollution and destruction events caused by human activities or force majeure within our company, including waste gas, wastewater, solid waste (including hazardous waste), hazardous chemicals, etc.; environmental pollution accidents that endanger human health caused by natural disasters; and other serious pollution accidents that affect the water quality of drinking water sources.
If an environmental pollution accident occurs in our company, the material properties mainly include sewage, atmosphere, and hazardous chemicals; The types of accidents mainly include loss, theft, fire, water pollution, air pollution, etc.
Human operational errors, inadequate protection, and hidden dangers in workplace equipment and facilities are the main causes of accidents. When a sudden environmental pollution event occurs, immediately activate the emergency plan.
2、 Command structure and responsibilities
(1) Command structure
1. Company Commander in Chief
Chen Xizhang
2. Special Command Group
Commander in Chief: Peng Xiaomin
Deputy Commander in Chief: Zhang Shiqiang
3. Emergency summary members (including expert group members)
Sun Yonglu, Shi Wei, Li Xinliang, Zhang Sheng, Li Shaogang, Liu Wenqing, Sha Qingtao, Xiuzuo Building
(2) Responsibilities of the command organization
Responsible for the development and revision of this contingency plan; Establish a professional emergency rescue team, organize implementation and drills; Inspect and supervise the prevention measures for major accidents and various preparations for emergency rescue.
When a major accident occurs, the command group shall issue and release emergency rescue orders and signals; Rescue teams carry out rescue operations; Report the accident situation to superiors and neighboring units, and if necessary, send rescue requests to relevant units; Organize accident investigation and summarize emergency rescue experience and lessons learned.
3、 Preventive measures for accidents
Targeted preventive measures should be taken to prevent accidents from occurring based on the identified hazardous targets and their possible pathways that may lead to accidents. Various preventive measures must establish a responsibility system and be implemented by departments and individuals. Once a situation occurs, try to reduce the degree of harm as much as possible.
1. Management measures for chemical substances
(1) Departments and individuals using chemicals must strictly abide by various safety production systems and operating procedures to avoid accidents.
(2) Dangerous chemicals must be stored in dedicated warehouses. Each user unit must have a chemical hazardous material counter and assign a dedicated person to manage and distribute them. Any remaining chemical materials should be immediately stored after use.
(3) The specialized warehouse for hazardous chemicals shall comply with relevant safety and fire prevention regulations, and shall be equipped with corresponding safety facilities such as ventilation, explosion prevention, pressure relief, fire prevention, lightning protection, alarm, fire extinguishing, sun protection, temperature regulation, and protective embankments according to the type and nature of the goods.
(4) The hazardous chemical warehouse should be equipped with fire extinguishing equipment and ventilation and alarm devices in accordance with fire safety regulations.
(5) Departments and individuals using hazardous chemicals must properly dispose of and classify waste liquids in accordance with the provisions of the Environmental Protection Law, and cannot dispose of them arbitrarily. Natural neutralization must be carried out for acidic and alkaline waste liquid before discharge.
(6) For expired and unlabeled hazardous chemicals, the using unit shall pack and register them in a centralized manner, and report to the Environmental Protection Office. The Environmental Protection Office shall seek professional companies for processing.
(7) The use of compressed gas and liquefied gas should avoid causing fires.
A. Compressed gas, liquefied gas, or gas dissolved under pressure stored in a steel cylinder expands due to heat, and the pressure increases, which can cause the cylinder to explode;
B. Some compressed gases and liquefied gases may undergo chemical reactions and cause combustion and explosion when in contact with each other;
C. Oils and other combustible materials are highly susceptible to ignition and even explosion under the impact of high-pressure pure oxygen;
D. Compressed gas and liquefied gas not only have explosive properties, but also have flammability, combustibility, toxicity, and suffocation properties. They are prone to combustion, explosion, or poisoning accidents under external effects such as heat, impact, and vibration.
2. Other measures
(1) Popularize and improve personal self-help skills.
(2) Plan drills. Combining professional drills with comprehensive drills.
(3) Strengthen the management of environmental protection facilities, improve the operating procedures and maintenance systems of environmental protection facilities, and ensure the normal operation of equipment.
(4) Reasonably utilize water resources, try to achieve multi use or recycling of one water, reduce water consumption, and reduce sewage discharge.
A. Various toxic and harmful substances in experimental wastewater must be treated to meet the national wastewater discharge standards before being discharged.
B. Cut off waste oil and organic solvents, do not pour them into open ditches or sewers without treatment, and dispose of them according to national regulations for recycling.
C. The animal and vegetable oils in the wastewater of the cafeteria must be strictly controlled below the national discharge standards before discharge.
D. Strict protection should be provided for self provided water source wells, and no pollution sources, seepage wells, seepage pits, or open toilets are allowed within a diameter of 200 meters. Planting various vegetables and stacking garbage around water is not allowed. Disinfect drinking water, conduct regular laboratory tests, wash wells regularly, and protect drinking water sources.
(5) Burning of garbage, leaves, and other waste is prohibited.
4、 Accident handling procedures
Once an environmental pollution accident occurs, the accident situation should be immediately reported to the company. The report content includes the time and location of the accident, a brief description of the accident, the type and number of pollution sources, nature, number of casualties, preliminary estimates of direct economic losses, and emergency measures taken.
After receiving the order, members of the expert group should immediately rush to the scene and provide necessary technical guidance for accident handling based on the type, number, and nature of the pollution source, to prevent the expansion and spread of the accident, and to prevent the occurrence of secondary hazards. We need to organize the safe transfer of important materials and equipment on site, especially flammable, explosive, toxic, and corrosive equipment and appliances.
Members of the on-site command team should organize personal protection based on the degree and scope of harm, terrain and weather conditions, and enter the site to implement emergency measures. It is necessary to quickly clarify the types and nature of pollution accidents, the quantity of pollutants, and the extent of pollution caused. After comprehensive analysis, a scientific pollution disposal plan should be proposed to the special command group in a timely manner. After approval, it should be quickly implemented according to the task division, emergency and disposal procedures and norms, and the handling process and situation should be reported to the command group in a timely manner.
1. On site pollution control
(1) Take effective measures immediately. Cut off pollution sources, isolate pollution areas, and prevent pollution from spreading;
(2) Timely report or evacuate personnel who may be affected by pollution hazards;
(3) Participate in the treatment of individuals at risk.
2. On site investigation and reporting
(1) Survey of pollution accident sites;
(2) Technical investigation and evidence collection;
(3) Environmental monitoring: It is generally required that water pollution be detected within 4 hours, and air pollution be detected within 2 hours to determine the types of pollutants and their potential hazards; Quantitatively detect the concentration, degree, and range of pollutants within 24 hours, and issue a monitoring report; And adopt pollution tracking and monitoring until the pollution accident is handled and the pollution report is lifted.
5、 On site protection
The accident scene must be strictly protected. Everyone participating in rescue and rescue must strictly protect the accident scene. When it is necessary to move objects on site due to rescue, signs, photos, detailed records, and on-site maps must be made, and the main traces and physical evidence on site must be properly preserved.
6、 Organize accident investigation and revise contingency plans
Conduct on-site investigation work, adhere to the principle of seeking truth from facts in accident investigation, and adhere to the "four no let go" principle in accident handling, that is, do not let go until the cause of the accident is identified, do not let go until the person responsible for the accident is dealt with, do not let go until employees are educated, and do not let go until corrective measures are implemented.